XSPECT payload on XpoSat
|
XPoSat is the India’s first X-ray polarimetricmission launched on 1st January 2024 by PSLV C58 rocket from Sriharikota. The satellite carries twoco-aligned instruments, Polarization in X-rays (POLIX) and X-ray SPECtroscopy and Timing (XSPECT). POLIX will investigate the X-ray polarization in cosmic X-ray source in medium energy X-rays and XSPECT will carry out X-ray spectroscopy of these sourcesin soft X-ray band.
Science objectives of XSPECT:XSPECT will provide crucial information about X-ray spectral state evolution in bright X-ray binaries, long term changes in continuum emission and line fluxes, pulse-shape and pulse pe-riod evolution in X-ray pulsars. Large count rate handling capacity of XSPECT makes it ideal to probe the bright X-ray sources in soft X-rays which was not possible earlier by imaging X-ray CCDs. Some of the scientific objectives of XSPECT payload are;
Salient features of XSPECT payload:XSPECT has Swept Charge Devices (SCD) as its sensors, which are non-imaging CCD type of sensor, each device is of ~ 4 cm2 in geometric area. Total sixteen devices make up the payload. Two different FOV collimators are used, 7 devices with 30 x 30 and 8 devices with 20 x 20 FOV, to measure cosmic X-ray background as well as source flux of interest enabling it to correct for background for each observation independently. One of the detector is shielded by tantalum sheet to block X-rays and thus enabling it to measure the charged particle back-ground. 
Figure 1: (a) XSPECT payload detector package. Two such packages are mounted on the instrument deck of the spacecraft. (b) XSPECT electronics package As part of Performance Verification (PV) phase operation, XSPECT payload was pointed to-Cassiopeia A (CasA), a standard source in the sky used for Instrument evaluation. The ob-servation of the source started on 05 Jan 2024. This source is a supernova remnant, which shows many emission lines in X-rays corresponding to elements such as Magnesium (Mg), Silicon (Si), Sulphur (S), Argon (Ar), Calcium (Ca), and Iron (Fe) as major lines. 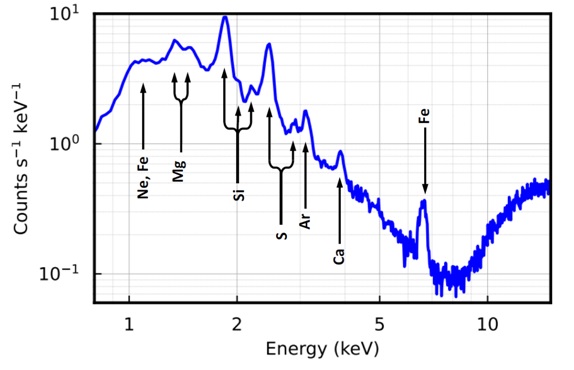
Figure 2: XSPECT sees supernova remnant Cassiopeia A (CasA). The spectrum in figure is as seen by the instrument, includes both Galactic Cosmic Ray (GCR) background and Cosmic X-ray Background (CXB).The flux above 8 keV is mainly due to both CXB and GCR. The spectrum shown in Figure is for a total integration time of 20 ksec collected over multiple orbits. |






