IRNSS - Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System
The IRNSS system architecture mainly consists of:
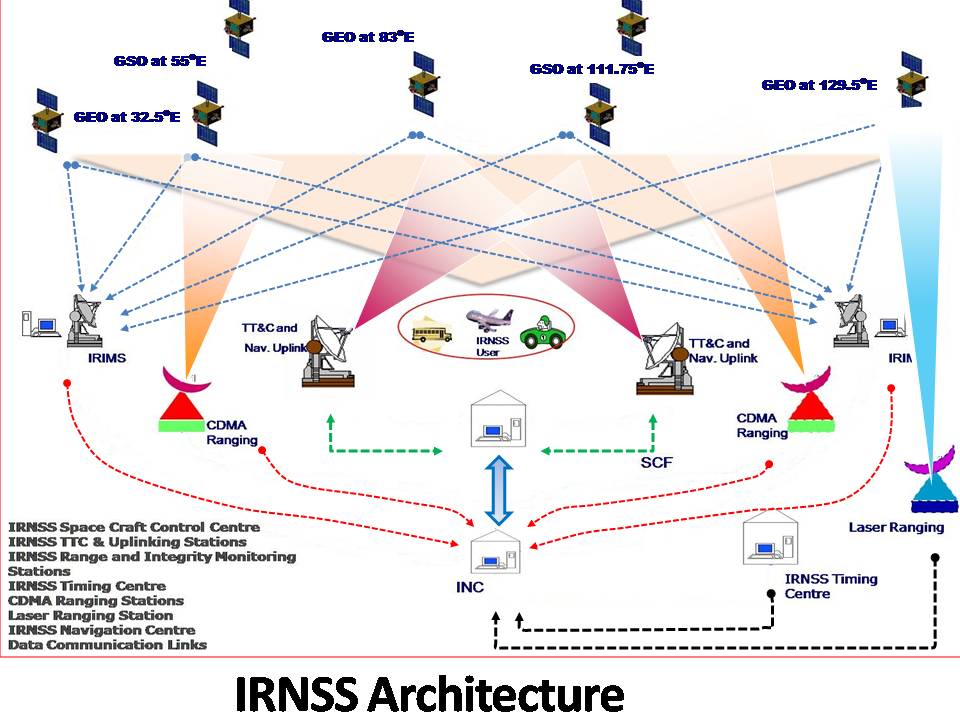
- Space Segment
- Ground Segment
- User Segment
Space Segment
The IRNSS space segment consists of 7 satellites (3 GEO and 4 GSO). The 3 GEOs will be located at 32.5o E, 83oE and 131o E and the 4 GSOs have their longitude crossings 55o E and 111.75o E (two in each plane).
IRNSS-1A spacecraft was launched on 1 July 2013. It was followed by launch of 5 more spacecrafts upto IRNSS-1F in the years 2014-16. The launch dates of the IRNSS satellites are given in table shown below. The space segment consists of seven IRNSS satellites with last satellite IRNSS-1G launched on 28th April, 2016.
The IRNSS Satellites are designed around I-1K bus with a dry mass of 600 Kg & a Lift off mass of 1425 Kg. It has a power generation capability of 1600 W. Three-axis control of the satellite with Yaw steering capability to optimize the use of Solar Panels and to support the thermal control of the satellite. The navigation payload transmits SPS & RS signals in L5 & S Bands. Highly stable Rubidium Atomic Frequency Standards (RAFS) are used on-board for generation of Navigation Signals.
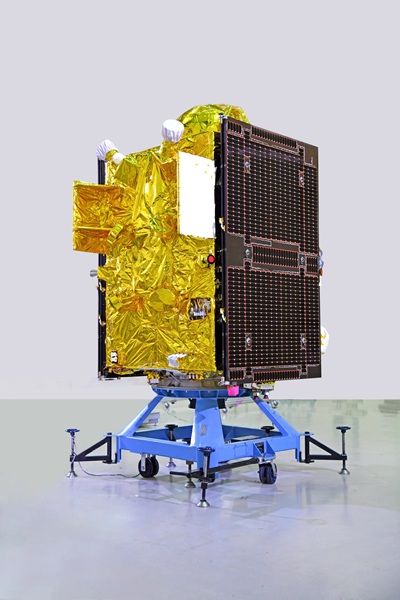

NVS-02 29-Jan-2025 GSLV-F15
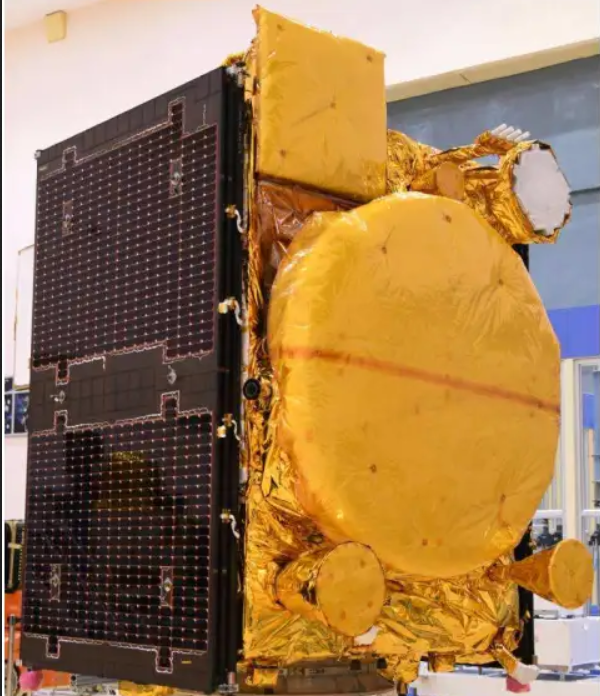

NVS-01 29-May-2023 GSLV-F12

IRNSS-1I 12-April-2018 PSLV-C41

IRNSS-1H 31-AUG-2017 PSLV-C39

IRNSS-1G 28-APR-2016 PSLV-C33

IRNSS-1F 10-MAR-2016 PSLV-C32

IRNSS-1E 20-JAN-2016 PSLV-C31

IRNSS-1D 28-MAR-2015 PSLV-C27

IRNSS-1C 15-OCT-2014 PSLV-C26

IRNSS-1B 04-APR-2014 PSLV-C24

IRNSS-1A 01-JUL-2013 PSLV-C22
Ground Segment Ground Segment is responsible for the maintenance and operation of the IRNSS constellation. The Ground segment comprises of:
-IRNSS Spacecraft Control Facility (IRSCF)
-ISRO Navigation Centre (INC)
-IRNSS Range and Integrity Monitoring Stations (IRIMS)
-IRNSS Network Timing Centre (IRNWT)
-IRNSS CDMA Ranging Stations (IRCDR)
-Laser Ranging Stations
-IRNSS Data Communication Network(IRDCN)
The INC established at Byalalu performs remote operations and data collection with all the ground stations. 14 IRIMS are currently operational and are supporting IRNSS operations. CDMA ranging is being carried out by the four IRCDR stations on regular basis for all the IRNSS satellites. The IRNWT has been established and is providing IRNSS system time with an accuracy of 20ns (2 sigma) w.r.t UTC. Laser ranging is being carried out with the support of ILRS stations around the world. Navigation Software is operational at INC since Aug 1st 2013. All the navigation parameters viz. satellite ephemeris, clock corrections, integrity parameters and secondary parameters viz. iono-delay corrections, time offsets w.r.t UTC and other GNSS, almanac, text message and earth orientation parameters are generated and uplinked the spacecrafts automatically. The IRDCN has established terrestrial and VSAT links between the ground stations. seven 7.2m FCA and two 11m FMA of IRSCF are currently operational for LEOP and on-orbit phases of IRNSS satellites.
User Segment
The User segment mainly consists of:
-Single frequency IRNSS receiver capable of receiving SPS/RS signal at L5 or S band frequency.
-A dual frequency IRNSS receiver capable of receiving SPS/RS signal in both L5 and S band frequencies.
Applications of IRNSS:
-Terrestrial, Aerial and Marine Navigation
-Disaster Management
-Vehicle tracking and fleet management
-Integration with mobile phones
-Visual and voice navigation for drivers
-Precise Timing
-Mapping and Geodetic data capture






